Penguin Census
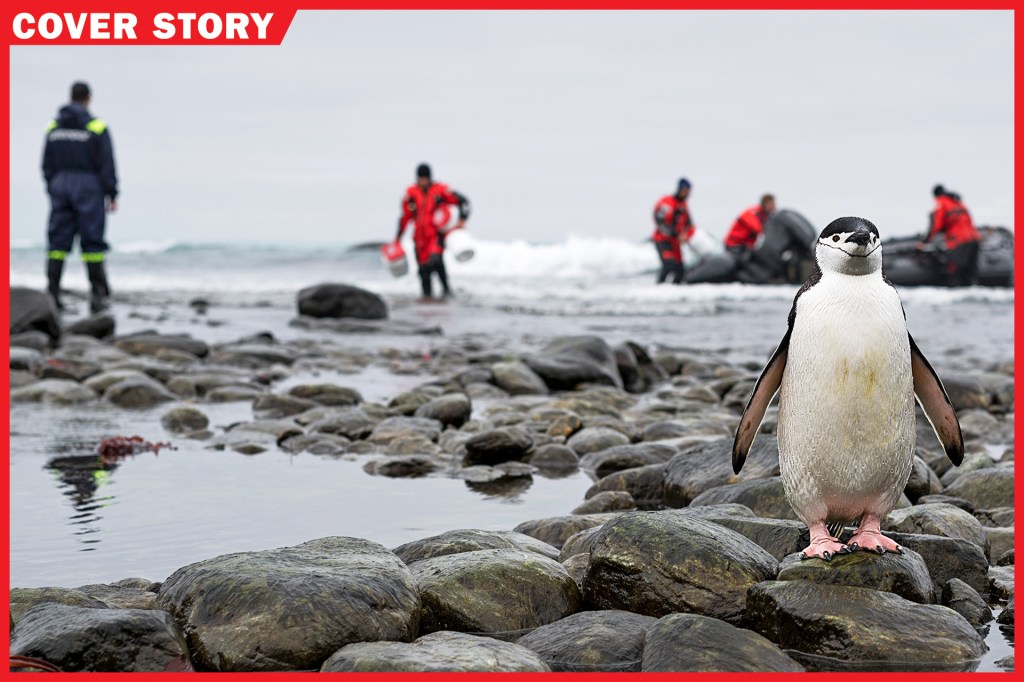

SNOW ISLAND, Antarctica—Click. Click click click. Click. Steve Forrest is a biologist. He’s standing at the top of a cliff. It’s on an island off the coast of the Antarctic Peninsula
peninsula
 DIANE555—GETTY IMAGES
a piece of land that sticks out into water
(noun)
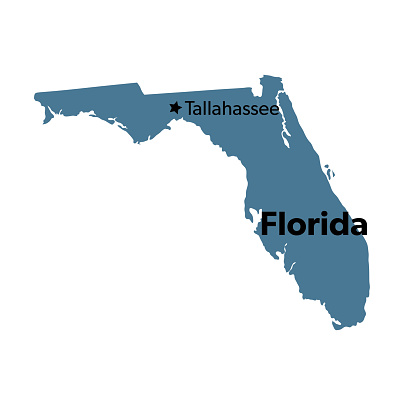
Florida is a peninsula.
. Below him are several hundred penguins and their chicks. Forrest’s job is to count every one of them with the metal clicker in his hand. It’s not easy. It’s snowing. The wind is howling. And the fluffy gray chicks won’t stay still.
DIANE555—GETTY IMAGES
a piece of land that sticks out into water
(noun)
Florida is a peninsula.
. Below him are several hundred penguins and their chicks. Forrest’s job is to count every one of them with the metal clicker in his hand. It’s not easy. It’s snowing. The wind is howling. And the fluffy gray chicks won’t stay still.
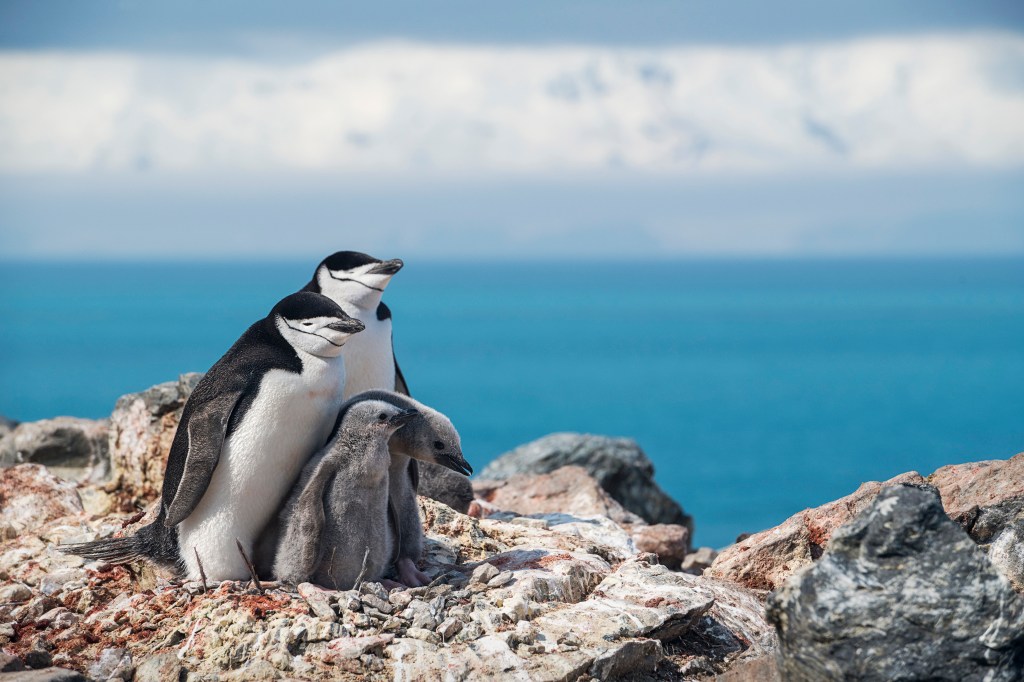

CHINSTRAP FAMILY Chinstrap penguins are named for the black band that runs around the throat of an adult bird.
CHRISTIAN ASLUND—GREENPEACEForrest has been coming to Antarctica every January for six years. He’s helping count the area’s chinstrap penguins. It’s part of a global penguin census
census
 JOHNER IMAGES/GETTY IMAGES
an official count of a population
(noun)
According to the last census, 412 people live in the town.
. This will help researchers better understand the Antarctic environment.
JOHNER IMAGES/GETTY IMAGES
an official count of a population
(noun)
According to the last census, 412 people live in the town.
. This will help researchers better understand the Antarctic environment.
Ocean Life
There used to be lots of chinstraps in Antarctica. But their numbers are declining. Why? “All the evidence we have points to climate change
climate change
 PAUL SOUDERS—GETTY IMAGES
changes in the Earth's weather patterns
(noun)
The sea ice that polar bears hunt from is melting due to climate change.
as being responsible,” Heather J. Lynch says. She designed the survey. Census team member Noah Strycker adds, “We know [climate change] is hitting the Antarctic Peninsula harder than practically anywhere else in the world.”
PAUL SOUDERS—GETTY IMAGES
changes in the Earth's weather patterns
(noun)
The sea ice that polar bears hunt from is melting due to climate change.
as being responsible,” Heather J. Lynch says. She designed the survey. Census team member Noah Strycker adds, “We know [climate change] is hitting the Antarctic Peninsula harder than practically anywhere else in the world.”
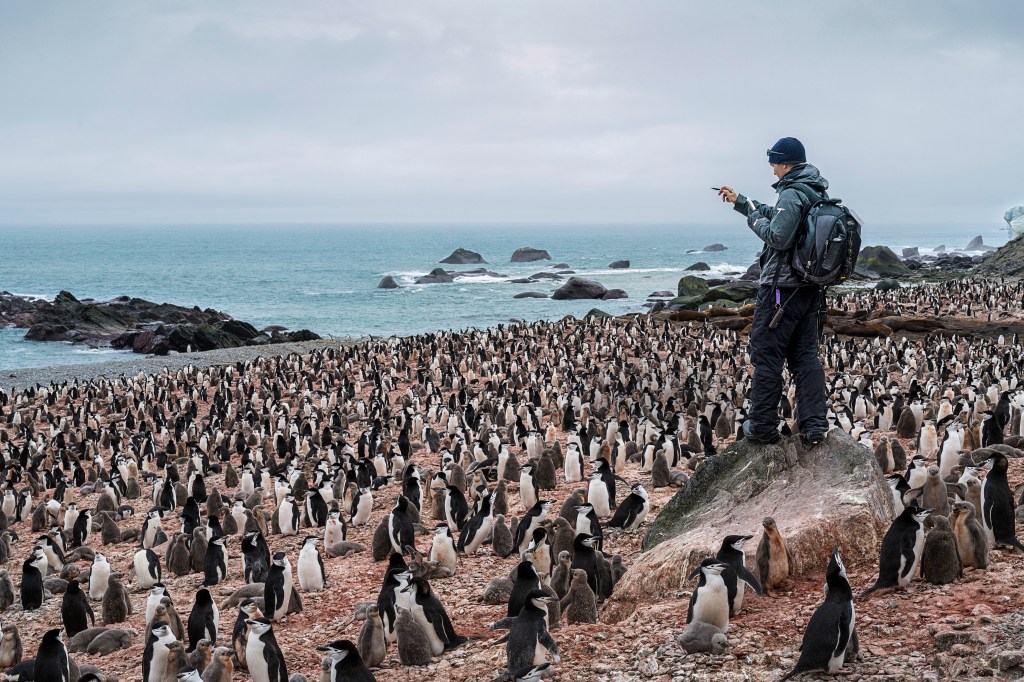

ONE, TWO, THREE Noah Strycker, of the penguin census team, counts chinstraps on Snow Island.
CHRISTIAN ASLUND—GREENPEACEScientists suspect that warming waters affect krill, the tiny creatures that chinstraps eat. This is bad for the ocean food chain
food chain
 GEORGE KARBUS PHOTOGRAPHY/GETTY IMAGES
an arrangement of living things in which each depends another for food
(noun)
Whales are at the top of the ocean's food chain.
. Whales eat krill. So do small fish that larger fish depend on. But krill are hard to study. So researchers focus on penguins. They’re easier to track. They return to the same spot each year to lay eggs. If chinstraps aren’t doing well, krill probably aren’t either. “Penguins give us an idea about what is going on in the ocean around us,” Forrest says.
GEORGE KARBUS PHOTOGRAPHY/GETTY IMAGES
an arrangement of living things in which each depends another for food
(noun)
Whales are at the top of the ocean's food chain.
. Whales eat krill. So do small fish that larger fish depend on. But krill are hard to study. So researchers focus on penguins. They’re easier to track. They return to the same spot each year to lay eggs. If chinstraps aren’t doing well, krill probably aren’t either. “Penguins give us an idea about what is going on in the ocean around us,” Forrest says.
That doesn’t mean counting penguins is easy. Chinstraps nest on rocky slopes to protect their eggs from predators
predator
 ALLAN DAVEY—GETTY IMAGES
an animal that kills and eats other animals to survive
(noun)
The great white shark is a fierce predator.
. Sometimes, scientists use binoculars to count the birds from a distance. Other times, the census requires them to brave freezing water in inflatable boats. “It’s miserable, it’s cold, but we love it,” Forrest says. “We get to go places where few people have ever set foot.”
ALLAN DAVEY—GETTY IMAGES
an animal that kills and eats other animals to survive
(noun)
The great white shark is a fierce predator.
. Sometimes, scientists use binoculars to count the birds from a distance. Other times, the census requires them to brave freezing water in inflatable boats. “It’s miserable, it’s cold, but we love it,” Forrest says. “We get to go places where few people have ever set foot.”
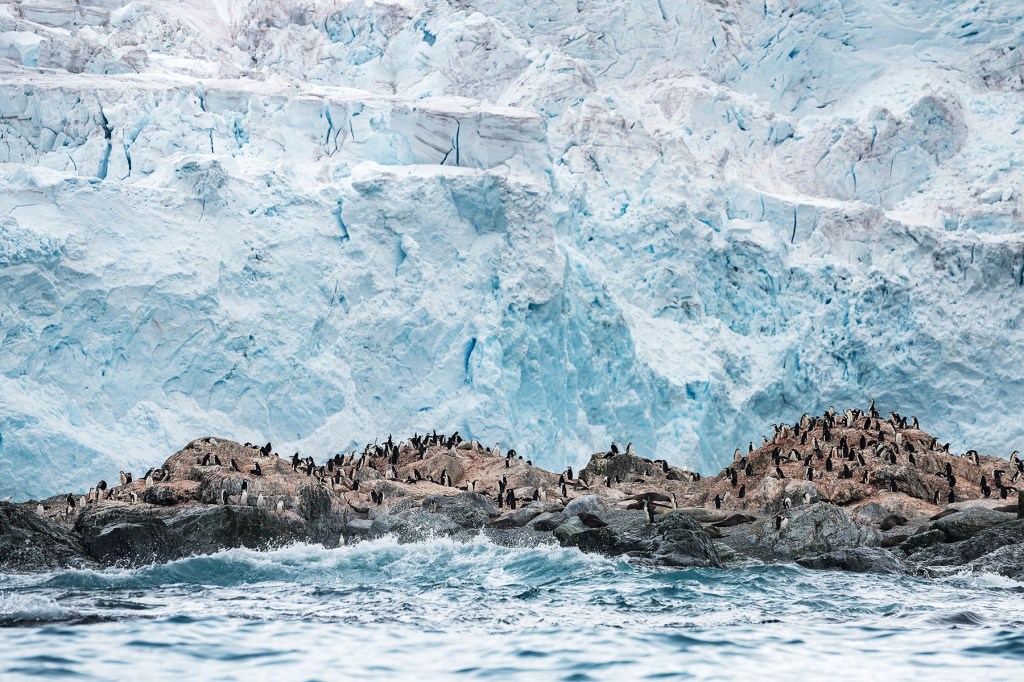

HÁBITAT SEVERO Aguas heladas turbulentas rodean la isla rocosa donde esta colonia de pingüinos hace su hogar.
CHRISTIAN ASLUND—GREENPEACEChinstraps are great climbers. So scientists must be too. And penguins aren’t always clean. Their nesting grounds are coated in guano, or droppings, so these places are slippery and smelly.
Drone Assistance
This year, Forrest’s research team got help from robotics engineers from Northeastern University. That’s in Boston, Massachusetts. The engineers fly a drone over a colony in order to take pictures. The team will use those photos to record the colony’s location and size. It will also use them to teach computers how to recognize penguin nests. One day, computers could count penguins.
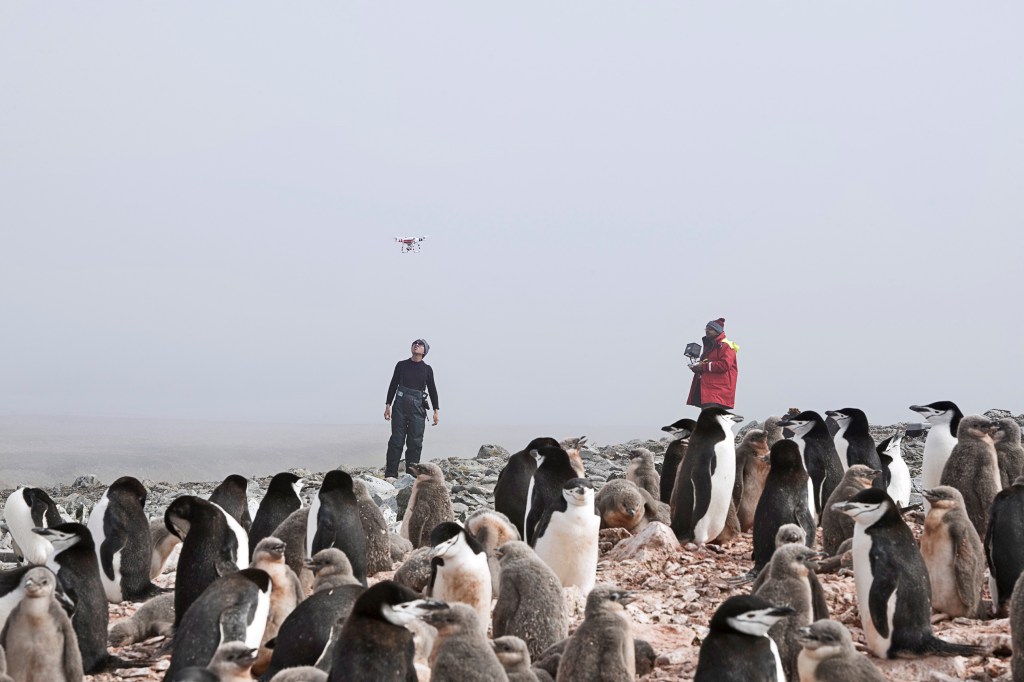

LOOK UP Two students from Northeastern University fly a drone over a colony of penguins.
CHRISTIAN ASLUND—GREENPEACECounting penguins is important, Forrest says. The more we learn, the more we know about krill and the ocean animals that depend on them. “What’s happening in the Antarctic is happening everywhere,” he says. “When we understand it, we can start fixing it.”













